Overstock-BB&B Search & Social Landing GMS Drive
Highlights
Business Results:
ROI of $1.3M, 2.5% increase to conversion, 11% decrease in bounce rate
Business Problem:
The business urgently needed to increase search engine landing page desktop conversion.
Methodologies & Processes
Existing data, literature review
Stakeholder interviews
Unmoderated qualitative interview
Prototype testing - click test
Heat Maps
Survey and click-data analysis
Artifact Created:
Figma presentation
Excel spreadsheet
Top 4 Findings and Recommendations
Tailor toward visitors’ needs for this specific funnel by adding other product recommendations to allow visitors to see more relevant products than just the primary product.
Improve visual hierarchy to highlight the main product.
Making price and reviews clickable to product pages.
Shorten the main products’ stack height to ensure the majority of the customers can see the additional product recommendations below.
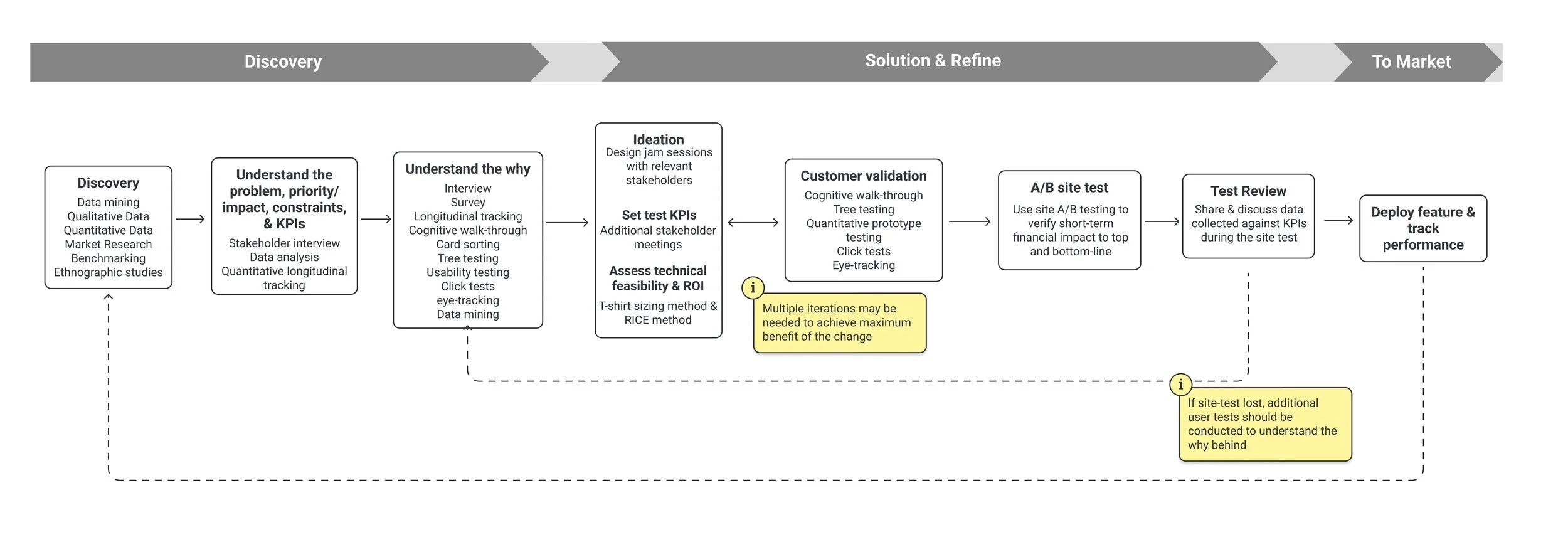
My Current Work Flow
Step-By-Step Details
I. Existing data, literature review
Connected with relevant stakeholders and used internal data tools to review the shoppers' and suppliers' current financial, demographic, attitudinal(e.x. site intercept), and behavioral data of the relevant features, pages.
Overstock used behavioral and attitudinal segmentation instead of demographic. Therefore, the demographic data is only served to double-check against the population. The demographic criteria will be kept relatively wide, except the gender distribution will be kept relatively even to reflect the population.
Behavioral data gave insight into whether any specific behavior attributes of this population would necessitate recruiting changes(in this case, no except for returning customers vs. new).
Overstock used a one-question simplified version to recruit participants with population-like attitudes. This question, however, is not comprehensive enough to be 100% accurate. When there is a concern with time or recruiting costs, this question is not used for initial screening; it will simply be added for post-analysis purposes. The following research did just this to adhere to the timeline and cost.
Review site-intercept data to understand funnel visitors’ intent. This is great contextual information to understand and prioritize the following research findings.
II. Stakeholder interviews
Interviews were conducted with stakeholders to understand the reasons behind targeting the search and social platform landing. Additional discussions were conducted with relevant stakeholders to design solutions.
III. Unmoderate qualitative interviews:
The goal
To understand how the Google search and social landing page are currently serving the visitors, what the visitors’ goals are, and what is missing for the visitors.
Recruiting:
12 participants were recruited who visited Overstock.com from Google search or social funnels to understand their needs and frustrations when landing on Overstock’s designated page for search and social funnels.
All participants were on desktop web since this was the funnel of concern.
6 participants reported that they used Google search as part of their online home-related items shopping experience and 6 reported they used Instagram/Facebook for such
Attitudinal segmentation questions were added for post-analysis purposes but not for screening purposes.
Age of the participants was kept broad(covering 90% of the visitor age distribution) with only gender distribution kept 50/50 to reflect the population.
IV. Presentation & solutioning
The goal is to come up with one testable solution that addresses the issues found to move forward.
Set up:
Relevant stakeholders from all related product functions and marketing functions were invited to the brainstorming session.
The session lasted 1 hour.
I first presented findings with videos and quotes from the qualitative interviews. The presentation also included a page of some potential recommended directions which leads to the brainstorming session.
The brainstorming session took the latter 30 minutes.
Each person generated ideas on their own then shared with the group. The attendee group voted on the solutions.
V. Prototype testing - Click test
The goals for the quantitative part of the prototype testing are to:
Understand if Overstock visitors can complete the desired action on the landing page in a similar time or faster manner.
Understand if the new page can better direct visitors toward GMS-generating click areas.
Recruiting:
336 participants who shopped at Overstock in the last month were recruited to complete tasks. Each was randomly selected to be exposed with only one variant.
Age of the participants was kept broad(covering 90% of the visitor age distribution) with only gender distribution kept 50/50 to reflect the population.
Participants reported either used Google search or used Instagram/Facebook as part of their online home-related items shopping experience
Set up:
Participants were exposed with either control or test. They will be invited to complete two tasks.
The test set up a scenario, using a navigation task, in which they have just landed from google search or social channel to this page by clicking on an item that interests them. The first task will ask the participant to click on the element that they would be interested in clicking looking at this page. The second task will ask them to to find the add-to-cart button. The tasks will be set up in a click test format to better capture the KPIs.
Analysis:
Usability and financial KPIs
Direct success and median time-on-task were collected for both tasks to analyze for difference between test and control.
A t-test was performed on the KPIs using 80% CI to check if test KPIs were different from control KPIs.
There was a significant increase in “clicks-to-product-pages” which is positively correlated to conversion. At the same time, there were no significant differences between control and test on time-to-first click for both tasks. There was no significant difference between the test and control’s success percentage for clicking add-to-cart. This means the design has no risk to the conversion potential of the page, and has the potential to achieve the goal of not impacting customer’s shopping experience.
*Replacement data
Control
Test
Analysis(cont’d)
heatmap: Using heat map to understand how participants clicks landed as a total group.
A quick visual inspection of the heatmap also showed any problematic clicks. In this case, some clicks went to review and price; neither will direct them to the product page. This was a missed opportunity to funnel customers and created a possible friction point.
Heatmap was also used to illustrate the click data results of the study.
Control Heatmap
Test Heatmap
VI. Tracking post-research:
A/B site test: A site test was conducted to verify the conversion impact of the change.
Periodic monthly and quarterly tracking of the key financial metrics.
Post-launch user behavioral tracking using heat mapping capabilities(Quantum Metric).
VII. If I had more time:
Conduct more detailed jobs-to-be-done research with opportunity size calculations to increase conversion by addressing the underlying needs.